Best Hearing Aids
Hearing Aids Basics: Choose What’s Best for you in 3 Easy Steps
Hearing aids are battery-operated devices that amplify sounds, helping individuals with hearing loss to hear and communicate effectively with other people. They all do the same thing, but what is the best hearing aid for You?
How Do Hearing Aids Work?
All hearing aids contain the following parts: microphone, amplifier, loudspeakers, battery, and computer-programmed microchip.
The microphone gathers sounds from the environment. Consequently, the computer chip processes these sounds and adjusts them to the desired volume.
The amplifier then magnifies these sounds and sends them through the loudspeakers. In turn, the loudspeakers send the sounds to the inner ear via a thin wire or tubing in the ear canal.
In the inner ear, all gathered sounds transform into electrical signals or impulses. This transformation is essential because sounds are interpreted or processed by our brain if they are in electrical impulse form.
The degree of amplification of your hearing aids greatly depends on the extent of damage of your inner ear’s sensory cells. The more damaged cells there are, the more severe your hearing loss would be. As such, you would need more amplification from your hearing aid.
Choosing the Right Hearing Aid for You
Be on the right track by following the following steps:
-
Rule out other causes of hearing loss.
There are instances when hearing loss are caused by other factors that may be remedied without using any hearing device. Have yourself checked by your doctor, preferably an otorhinolaryngologist, to rule out the presence of impacted ear wax or an ear infection. You won’t be needing any hearing aid if these are what’s causing your hearing loss because they’d go away with treatment or medications.
-
Get a referral from your physician or audiologist.
If your physician finds that your hearing loss is due to the damage of your sensory cells in your inner ear, he or an audiologist may give a referral on what particular type of hearing aid is suitable for you.
-
Familiarise yourself with all hearing aid types or styles.
With so many hearing aids available in the market today, you have to be more prudent in choosing the one that will most suit your needs. To date, there are five major types or categories of hearing aids to choose from:
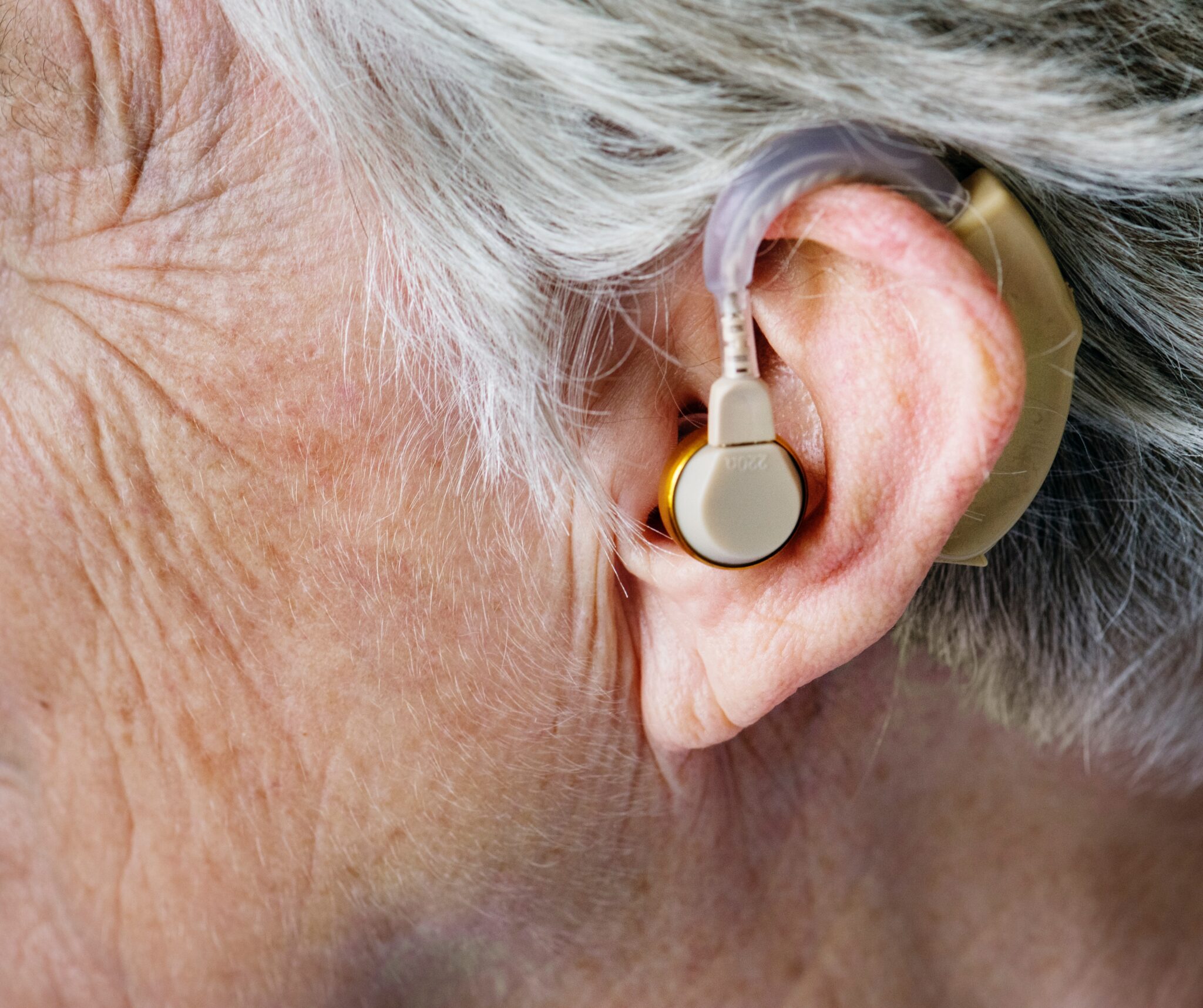
- Traditional Behind-the-Ear Hearing Aid (BTE)
This is considered the most suitable for people with severe hearing loss. They contain flexible features and are easy to control. Since most of its electronic parts are enclosed with a plastic case, cleaning is never a problem.
Nonetheless, this catches a lot of ear wax and sweat, which could be a con for some.
- Mini-Behind-the-Ear Hearing Aid (mBTE)
This type is hardly visible and is comfortable to wear. Also, it doesn’t give an obstructed or plugged-up feeling, which BTE users usually experience. However, this hearing aid is prone to ear wax and moisture accumulation, which may be cumbersome for some.
- Completely-in-the-Canal Hearing Aid (CIC)
This type is small enough to be worn deep into the ear canal. Hence, this becomes a good option for those who prefer a more concealed hearing aid.
One of its disadvantages is its small battery and limited battery life. Just like the mBTE and BTE, this is also prone to ear wax and moisture accumulation.
- In-the-Canal Hearing Aid (ITC)
ITC is not readily visible, which, for some, is a plus. However, just like other completely-in-the-canal categories, patients often complain of discomfort from using this.
- Traditional In-the-Ear Hearing Aid (ITE)
This type may be more visible than the rest of its counterparts, but it is large enough to contain more hearing aid features. This is also easier and more comfortable to wear.
Certainly, hearing aids cannot revert your hearing back to normal. However, by following this simple guide, you can choose the hearing aid that will meet your needs in terms of capability and comfort. Choose your hearing aid wisely by comparing the different products available on the market today here at Makes Cents.




